Orthopaedist
private consultations:
bow. Karol Blok - specialist in orthopedics and traumatology of the musculoskeletal system
bow. Piotr Bondarenko - specialist in orthopedics and traumatology of the musculoskeletal system
We diagnose and treat: :
- inflammation of the musculoskeletal system (inflammation of tendons, joints, bursae, etc.)
- acute and chronic back pain
- overload syndromes of the musculoskeletal system (tennis elbow, golfer's elbow, jumper's knee)
- traumatic and post-traumatic conditions (bruises, sprains, sprains, fractures)
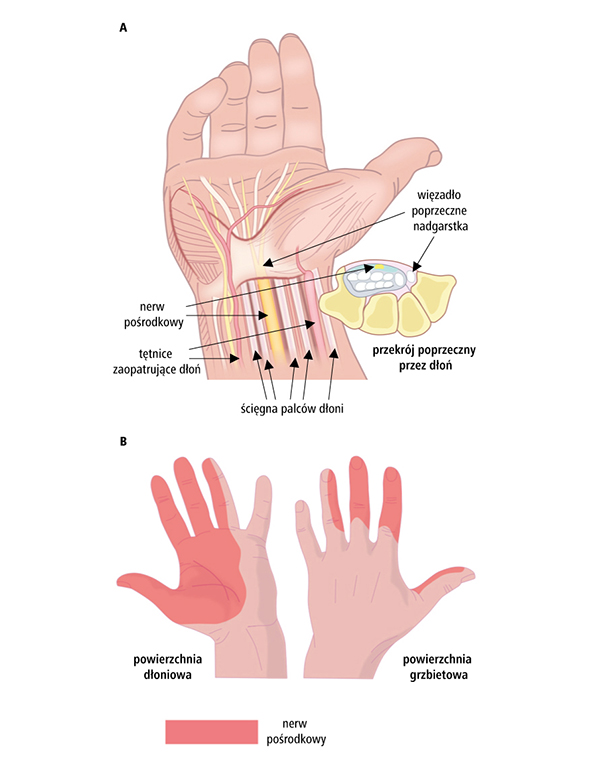
- peripheral nerve compression syndromes (carpal tunnel syndrome, Guyon's canal syndrome, ulnar nerve groove syndrome)
- degenerative changes in the joints, swelling of the knees and joints, posture defects
We perform treatments:
- joint locks
- joint punctures
- application of hyaluronic acid
- platelet-rich plasma (PRP)
- orthokine therapy
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- snapping fingers
- Dupuytren's contracture
- ganglion excision
Hyaluronic acid
In the case of damage to the joint (as a result of its injury or degenerative disease), the elasticity and viscosity of the synovial fluid decreases, which reduces the mobility of the joint, causes pain and causes destruction of the joint cartilage.
Supplementing the synovial fluid by injecting purified hyaluronic acid into the joint (Biolevox Ha) improves its elasticity and viscosity, as a result of which, after the first treatment cycle, the mobility of the joint will increase and the level of pain experienced as a result of the degeneration of the articular cartilage will be reduced.
The effects of the treatment last for many months.
The specialist doctor decides about the number of injections in the therapy.

PRP (Platelet Rich Plasma) PLATElet RICH PLASM
The method of injection of platelet-rich plasma used in orthopedics is based on the use of the body's ability to regenerate.
Stimulating our own cells to regenerate is possible by taking our own blood. From 1 to 3 tubes are collected under vacuum.
In a laboratory test tube, the blood is centrifuged, separating the platelet-rich plasma from the red blood cells. PRP is administered by intra-articular or periarticular injection (i.e. by injection), if necessary under ultrasound guidance.
The procedure carried out in the office is quick and safe for the patient, because thanks to the use of factors from his own blood, an allergic reaction is excluded.
Efficacy of platelet-rich plasma in orthopedics.
PRP works by activating platelets contained in platelet-rich plasma to produce specific growth factors.
The effect is the stimulation of tissue regeneration processes, the formation of new blood vessels and the production of collagen.
Thanks to this method, damaged tissues and structures can be restored in cases such as:
- tennis elbow,
- golfer's elbow,
- delayed bone union,
- heel spurs,
- jumper's knee,
- tendon and muscle damage
- Achilles tendon degeneration.
Orthokine® Therapy



Orthokine is a fully autologous, effective, safe and clinically proven form of treatment.
What is the therapy?
It consists in administering to the patient in the form of an injection of his own multiplied, concentrated anti-inflammatory proteins produced from blood previously collected from him. No foreign substances are introduced into the body, only proteins derived from the patient's own blood. It has been used since 1998. More than 500,000 serum injections have already been performed in over 500 licensed centers around the world.
Orthokine® therapy causes:
- Inhibition/slowing down of the inflammatory process of joints characteristic of degenerative changes
- Inhibition/slowdown of cartilage and tissue destruction
- Inhibition of inflammation of the nerve and its surroundings in the case of back pain nerve damage in the case of back pain
- Direct action on the site of pain: limitation and reduction of pain intensity
- Improvement of muscle and tendon function after injuries
The effectiveness of Orthokine® therapy:
The effectiveness of Orthokine® therapy and its tolerance by patients have been clinically proven and scientifically confirmed in clinical trials. This natural, biological method of treatment is an example of the application of molecular biology in orthopedics. Careful observation of patients in many years of research, results of preclinical tests and clinical trials, doctors' experience confirm the effectiveness and good tolerance of Orthokine® therapy by patients.
Carpal tunnel syndrome
What is Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a set of symptoms associated with compression of the median nerve in the carpal tunnel (see figure below). This disease belongs to compression neuropathies, which means that mechanical pressure is responsible for unfavorable changes in the nerve.
Surgery.
During the surgical procedure, the carpal tunnel is released by cutting the degenerated flexor retinaculum, which causes pressure on the median nerve. This relieves the symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome.
The incision is made at the base of the hand. This allows the doctor to see the transverse carpal ligament (flexor retinaculum). After cutting the ligament, the surgical wound is sutured with skin sutures.
The procedure is performed under local anesthesia, after the procedure you can go home the same day.
What to expect after surgery:
After the procedure, the hand is wrapped. The sutures are removed after approx. 10 days. Pain and numbness may subside immediately after the procedure, or it may take several months. Try to avoid heavy hand use for up to 3 months.
If you have surgery on your dominant hand and perform repetitive activities at work, you may be able to return to work in 6 to 8 weeks. Repetitive movements include typing on a computer or working on an assembly line. If you had surgery on the other hand and you are not doing repetitive work activities, you may be able to return to work within 4 weeks.
When Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Surgery is Considered:
If symptoms are present after a long period of non - surgical treatment. In general, surgery is considered if injections of steroids and a few weeks of resting the wrist do not have a therapeutic effect.
If the EMG examination shows nerve damage, surgery is necessary.
Severe symptoms (such as prolonged loss of feeling or coordination in the fingers or hand, or lack of strength in the thumb) limit everyday activities.
Damage to the median nerve (visible on EMG and loss of hand or finger function) threatens irreversible loss of function.
Tumors or other growths must be removed.
After surgery
Most people experience less or no symptoms of hand pain and numbness right after carpal tunnel surgery.
In rare cases, symptoms of pain and numbness (the most common complication) may return, or there may be a temporary loss of strength when pinching or grasping an object due to transverse carpal ligament severing.
If the thumb muscles have been severely weakened or severed, hand strength and function may be limited even after surgery.
A snapping finger
The disease is inflammation of the tendon sheath of the flexor finger of the hand. The tissue surrounding the tendons that bend the fingers thickens significantly, which prevents the tendons from sliding freely. This is manifested by the inability to straighten the finger freely. Initially, the ailment occurs after a period of rest, most often in the morning, and with the development of the disease, after each bend. There is also swelling at the base of the fingers. We straighten the locking finger "by force" with accompanying pain and a characteristic crack.
Surgical procedure - slamming finger
Description of the procedure:
The operation is performed in an ischemic field obtained by placing a tourniquet on the arm. The procedure consists in surgical cutting or removal of the inflamed sheath of the finger flexor tendon and causing free movement of the finger flexor tendon.
Performing a snapping thumb operation does not guarantee the resolution of existing ailments. The final effect of treatment is closely related to compliance with medical recommendations and the performance of a full cycle of rehabilitation treatments individually tailored to each patient.
After treatment:
- The hand can be worn in a sling for several days - this will reduce hand swelling and pain.
- You may experience hand pain and numbness in your fingers for a few days - painkillers are recommended - according to your information about the dose of the medicine and how to take it.
- After the operation, the night pain in the hand should subside.
- On the first day after the operation, there is a slight congestion of the dressing.
- On the second day after the operation, you should start exercising the operated trigger finger as much as the dressing allows. This prevents the stiffness of the fingers and the formation of hand swelling. You should also exercise your elbow and shoulder.
- The sutures are removed on the 10th day after the operation. Until then, try not to lower your hands day and night.
- The operated hand should be spared for 6 weeks (do not perform work requiring a forceful grip of the hand).
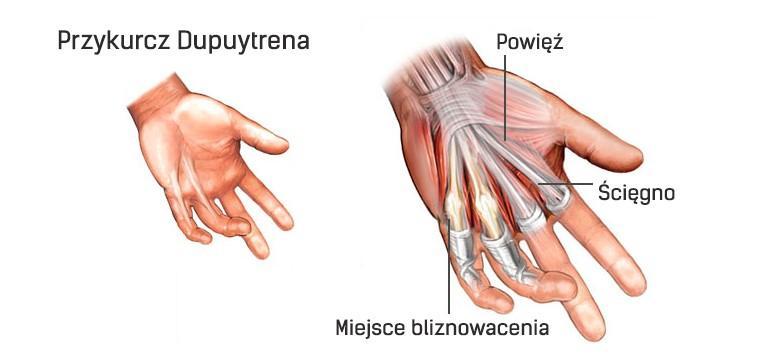
Dupuytren's contracture
This is a flexion contracture of the fingers, which is much more common in men. It most often affects the palmar surface of the hand. In about 25-60% of cases, it is genetically determined. It is characterized by the appearance of a small bump or thickening in the palm area.
Treatment:
Restoring the hand to function (or reducing the degree of contracture) is possible only as a result of the procedure. It is performed under local or general anesthesia. A tourniquet is used as anesthesia, causing the effect of ischemia of the operated limb.
The orthopedic surgeon cuts/cuts overgrown strands that cause contractions. The wound is closed with sutures and secured with a dressing (sometimes a plaster splint is used). If there is a need to drain the postoperative wound, a tube is inserted under the skin that drains the blood into a plastic bottle (the drain is removed the day after the procedure). Sutures and immobilization are removed after approx. 2 weeks. Convalescence lasts about a month.
Treatment complications:
- hematomas and swelling of the hands,
- skin necrosis around the postoperative wound,
- infections,
- limited mobility of the joints of the hands,
- chronic pain in the postoperative site,
- nerve damage
- recurrence of the disease (if it was operated on at a late stage).
Rehabilitation:
Hand exercises play a key role in returning to full fitness after surgery. They allow for tissue regeneration, scar reduction and regaining finger mobility. Rehabilitation can also be initiated at an early stage of contracture to prevent its further development.
Ganglion excision
What is a ganglion?
Ganglions (gelatinous cysts) are the most common nodules in the hands. They are not malignant changes and in most cases they are harmless. They occur in various locations, but most often they form on the dorsal surface of the wrist. At first glance, a ganglion may look like a protruding wrist bone. Ganglions require ultrasound diagnosis of the wrist or hand.
Ganglions are filled with fluid and can appear, disappear or change size in a short time. In many cases, a jellyfish cyst does not require treatment, but it always requires medical verification. However, if the cyst is painful, impairs mobility, or is a cosmetic defect, there are several treatment options.
Ganglion treatment:
The basis of ganglion treatment is the elimination of inflammation within the joint. The first step should be to relieve the burden by limiting movement in the place where the lesion is formed, for example with a sling, splint or orthosis.
The next step in the treatment of the ganglion is its puncture and draining the lesion from the residual fluid along with the supply of corticosteroids, which gives the possibility of overgrowth and the formation of an internal scar. This procedure is performed under sterile conditions, under anesthesia and, if necessary, under ultrasound guidance. However, it is believed that the treatment is not entirely effective.
Surgical removal of the ganglion may be necessary if conservative treatment is ineffective or relapses follow. During the procedure, a fragment of the joint or tendon capsule is excised. Ganglion surgery is performed under local anesthesia with a small skin incision. After it is carried out, the joint is immobilized for a few days. Return to normal activity occurs after about 6 weeks, and physiotherapeutic procedures are performed in the postoperative period.
contact
Address
-
- ORSMED
Przemysław Gliszczyński, Agnieszka Gemba spółka jawna
ul.Przemysłowa 3,
89-600 Chojnice
- ORSMED
Opening hours
-
- Mon - Fri: 9:00 AM - 6:00 PM
- Sat: 9:00 AM - 1:00 PM